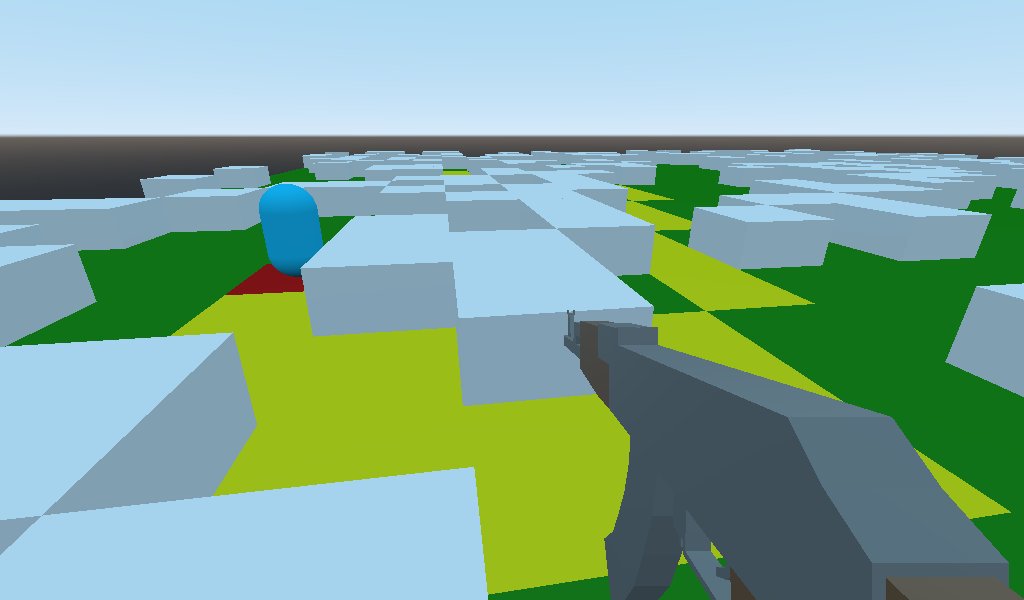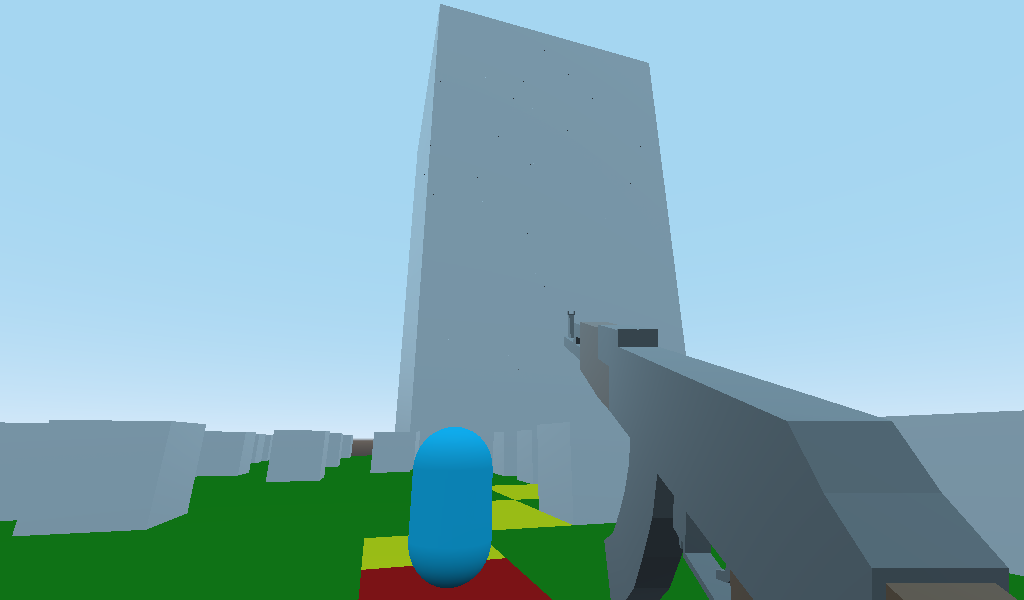
This simulator implements the A* pathfinding algorithm for AI bots to navigate an environment consisting of random blocks / walls and high-rise buildings.
Creating the map
To create the map, I had to first create a blank 2D grid map and then add blocks / walls to a random (x,z) node position.
func generate_map() -> void:
# create blank map
for x in range(map_size):
for z in range(map_size):
var key_position = Vector3(x, 0, z)
create_floor(x, 0, z, key_position)
# add walls
for _x in range(floor(map_size * map_size * percent_walls)):
var rand_num_x: int = rng.randi_range(0, map_size - 1)
var rand_num_z: int = rng.randi_range(0, map_size - 1)
var rand_key_position: Vector3 = Vector3(rand_num_x, 0, rand_num_z)
create_wall(rand_num_x, 0, rand_num_z, rand_key_position)Connecting the nodes
Next is to connect each node position to its surrounding nodes that isn’t a block / wall.
However there are a few edge cases to take account when connecting the nodes:
- Do not provide a path to a point that is completely enclosed in blocks
- Do not provide a path without jumping across a diagonal corner of two blocks
- Do not provide a path that cuts corners of blocks / walls
func create_astar_map() -> void:
# loop through all grid cells
for x in range(map_size):
for z in range(map_size):
var center_position = Vector3(x, 0, z)
if not (center_position in gridmap_index.keys()):
continue
connect_surrounding_cells(center_position)
func connect_surrounding_cells(center_position: Vector3) -> void:
for x in [-1, 0, 1]:
for z in [-1, 0, 1]:
if x == 0 and z == 0:
continue
var target_position = center_position + Vector3(x, 0, z)
if not (target_position in gridmap_index.keys()):
continue
var source_index = gridmap_index[center_position]
var target_index = gridmap_index[target_position]
var diagonal_status: bool = has_diagonal_walls(center_position, target_position)
if (diagonal_status):
continue
astar.connect_points(source_index, target_index, true)Implementing the A* algorithm
import heapq
def astar(start, goal, graph, heuristic):
"""
A* algorithm implementation.
Args:
start: Start node.
goal: Goal node.
graph: Graph represented as a dictionary of dictionaries.
heuristic: Heuristic function.
Returns:
Path from start to goal.
"""
# Initialize open and closed lists.
open_list = [(0, start)]
closed_list = set()
# Initialize g-scores and parents.
g_scores = {start: 0}
parents = {start: None}
while open_list:
# Get node with lowest f-score.
f_score, current = heapq.heappop(open_list)
# Check if goal node is reached.
if current == goal:
path = []
while current:
path.append(current)
current = parents[current]
return path[::-1]
# Add current node to closed list.
closed_list.add(current)
# Explore neighbors.
for neighbor in graph[current]:
# Ignore neighbors in closed list.
if neighbor in closed_list:
continue
# Calculate tentative g-score.
tentative_g_score = g_scores[current] + graph[current][neighbor]
# Add neighbor to open list if not already in it.
if neighbor not in [n[1] for n in open_list]:
heapq.heappush(open_list, (tentative_g_score + heuristic(neighbor, goal), neighbor))
# Update neighbor's g-score if new path is better.
elif tentative_g_score < g_scores[neighbor]:
index = [n[1] for n in open_list].index(neighbor)
open_list[index] = (tentative_g_score + heuristic(neighbor, goal), neighbor)
# Update parent and g-score.
parents[neighbor] = current
g_scores[neighbor] = tentative_g_score
# No path found.
return NoneGenerate the path for the bot
func generate_path() -> void:
# generate two random points
for gen_run in range(2):
var has_two_points = false
var rand_cell_pos: Vector3 = Vector3()
while not (has_two_points):
var rand_num_x: int = rng.randi_range(0, map_size - 1)
var rand_num_z: int = rng.randi_range(0, map_size - 1)
rand_cell_pos = Vector3(rand_num_x, 0, rand_num_z)
if (gen_run == 1 and city_cellpath.start != rand_cell_pos and gridmap_cells[rand_cell_pos] == CELL.FLOOR):
has_two_points = true
if (gen_run == 0 and gridmap_cells[rand_cell_pos] == CELL.FLOOR):
has_two_points = true
if (gen_run == 0):
city_cellpath.start = rand_cell_pos
else:
city_cellpath.end = rand_cell_pos
var start_path = gridmap_index[city_cellpath.start]
var end_path = gridmap_index[city_cellpath.end]
bot_path_list = astar.get_id_path(start_path, end_path)
# clear previous waypoint position list
waypoint_pos_list.clear()
# go through the path list
for index in bot_path_list:
var pos_x = gridmap_position[index].x
var pos_z = gridmap_position[index].z
var path_pos = Vector3(pos_x, 0, pos_z)
if (path_pos == city_cellpath.start):
city_gridmap.set_cell_item(pos_x, 0, pos_z, CELL.START, 0)
elif (path_pos == city_cellpath.end):
city_gridmap.set_cell_item(pos_x, 0, pos_z, CELL.END, 0)
else:
city_gridmap.set_cell_item(pos_x, 0, pos_z, CELL.LIGHT, 0)
# create waypoint list
waypoint_pos_list.append(gridmap_position[index])